Table of Contents
Introduction:
In today’s fast-paced technological landscape, two terms that frequently feature in discussions are “edge computing” and “cloud computing.” While both these concepts involve computing resources, they serve distinct purposes and play essential roles in modern network architecture. Businesses and individuals must understand the differences between edge computing and cloud computing to optimize their digital infrastructure fully. In this blog post, we will delve deeper into the nuances of each concept, their unique features, and how they complement each other to help you make informed decisions about your network infrastructure.
What is Edge Computing?

Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data near the source of data generation rather than relying on centralized data centers. In edge computing, computation is performed on local devices or edge servers, which are situated closer to where the data is created. This proximity minimizes latency and enables real-time data processing, making it ideal for applications requiring immediate insights or responses.
Key Points about Edge Computing:
- Low Latency: By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the time it takes for data to travel, resulting in lower latency and faster response times.
- Data Locality: Edge computing allows organizations to keep sensitive data within their premises, enhancing privacy and security compliance.
- Scalability: Edge computing architecture can scale horizontally by adding more edge devices or servers as needed, ensuring flexibility and agility.
- Offline Operation: Edge devices are designed to operate autonomously, even when disconnected from the central network, ensuring continuity in remote or intermittent connectivity environments.
Understanding Cloud Computing:
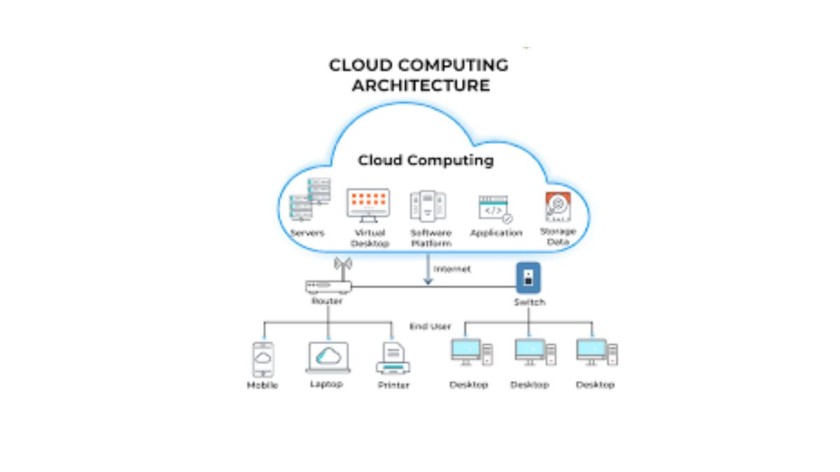
Cloud computing, on the other hand, involves the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet (“the cloud”). Unlike edge computing, which focuses on local processing, cloud computing relies on remote servers hosted in data centers operated by third-party providers.
Key Points about Cloud Computing:
- Scalability: Cloud computing offers virtually limitless scalability, allowing businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand without the need for significant upfront investment in hardware.
- Accessibility: Cloud services can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work, collaboration, and seamless data access.
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud computing follows a pay-as-you-go model, where users only pay for the resources they consume, resulting in cost savings and resource optimization.
- Centralized Management: Cloud computing platforms provide centralized management of resources, enabling easy deployment, monitoring, and management of applications and services.
The Importance of Knowing the Difference:
Understanding the difference between edge computing and cloud computing is essential for organizations seeking to optimize their digital infrastructure and harness the full potential of modern technology. While edge computing offers advantages in terms of low latency, data privacy, and real-time processing, cloud computing provides scalability, accessibility, and centralized management.
Conclusion:
both edge computing and cloud computing are essential components of modern network architecture, each offering unique advantages and serving distinct use cases. By understanding their differences and complementary nature, organizations can develop robust, agile, and efficient infrastructures capable of meeting the diverse demands of the digital era. Whether it’s real-time data processing at the edge or scalable cloud resources for centralized management, the synergy between edge computing and cloud computing paves the way for innovation and transformative possibilities in the ever-evolving landscape of technology.
Read more- Top 10 Laptop Accessories Brands in India
FAQ:
(1) What are ideal scenarios for using edge computing solutions?
Real-time data processing in IoT applications such as autonomous vehicles or smart manufacturing where low latency is critical.
(2) How can edge computing improve sustainability?
By reducing the need for data transmission to centralized data centers, thus minimizing energy consumption and carbon footprint associated with data processing.
(3) Describe the relationship between edge computing and cloud computing.
Edge computing complements cloud computing by bringing computation closer to the data source, reducing latency, while cloud computing provides scalability and centralized management of resources.
(4) What is Accenture’s most important advantage with 5G and edge computing?
Accenture’s extensive expertise in both technologies allows them to provide comprehensive solutions that leverage high-speed connectivity and localized processing to drive innovation across industries.
(5) What is the underlying concept of edge computing?
Edge computing is based on processing data closer to the source of data generation, reducing distance and enabling faster response times and real-time insights.
(6) How does edge computing reduce latency for end users?
By processing data locally at the edge of the network, edge computing reduces the distance data needs to travel, minimizing latency for faster response times.
(7) What recent innovation in edge computing is enhanced by 5G?
Multi-access edge computing (MEC) leverages 5G networks to deploy computing resources at the edge, enabling ultra-low latency for applications like augmented reality and real-time analytics.
(8) In which type of situation would it make sense to use edge computing?
Applications requiring real-time processing and low latency, such as IoT deployments or augmented reality experiences, benefit most from edge computing.
(9) What factors have made edge computing cheaper and easier?
Advances in hardware technology, networking infrastructure, and standardized frameworks have contributed to making edge computing more cost-effective and accessible.
(10) What is edge computing in simple terms?
Edge computing is a decentralized approach to data processing that brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation for faster processing and real-time insights.

1 thought on “Difference Between Edge Computing and Cloud Computing”