Table of Contents
Introduction:
Few technological advancements have been as vital to our society as the evolution of computer networks. This journey has spanned decades of innovation and adaptation and has created a web of connectivity that binds the world in an unprecedented exchange of information and communication. We invite you to join us as we explore this rich history and nuanced development that has shaped the evolution of computer networks, from their early beginnings to the dynamic landscape of the digital era.
Few technological advancements have been as instrumental to our society as the evolution of computer networks. These networks enable us to connect, communicate, and share information with anyone, anywhere in the world, in real time. The journey of computer networks spans decades of innovation and adaptation and has been a key driver of progress in countless industries, from healthcare to finance to entertainment.
The history of computer networks began in the 1960s with the development of a primitive network called ARPANET by the United States Department of Defense. ARPANET was the precursor to the modern-day internet, and its development paved the way for the development of more sophisticated networks that could connect computers in different locations.
Over the years, computer networks have evolved in many ways. Advancements in hardware, software, and protocols have enabled networks to become faster, more reliable, and more secure. The development of wireless networking has made it possible to connect devices without the need for physical cables, while the adoption of cloud computing has enabled users to access computing resources from anywhere in the world with an internet connection. Today, computer networks are an essential part of our daily lives. They enable us to work, learn, and play in once unimaginable ways.
We can collaborate with colleagues on the other side of the globe, stream movies and TV shows on demand, and access information on any topic with just a few clicks. As we continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, the evolution of computer networks will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of our world.
Evolution of Computer Network:
(1) The Genesis: Seeds of Connectivity
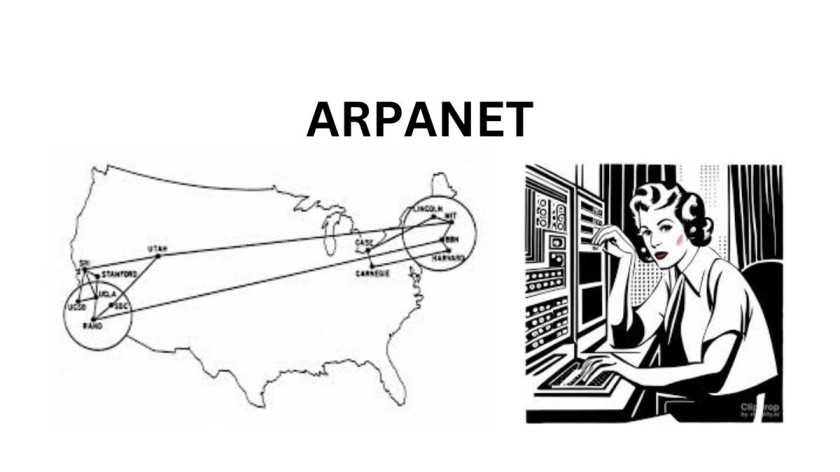
At the dawn of the computer age, when mainframes filled entire rooms and computing power was a luxury, the seeds of connectivity were sown. The ambitious visionaries of the mid-20th century laid the groundwork for what would become the backbone of modern networking. Among them stood the pioneers of ARPANET, a groundbreaking project initiated by the U.S. Department of Defense in the late 1960s. ARPANET, though modest in its inception, heralded the birth of packet-switching technology and the foundational principles of interconnecting disparate systems—a precursor to the internet as we know it.
(2) Protocols and Standards: Building Blocks of Communication
As networks expanded and diversified, the need for standardized protocols became paramount. Enter TCP/IP—the bedrock of modern networking. Conceived in the 1970s, TCP/IP provided the blueprint for data transmission across heterogeneous networks, enabling seamless communication between computers of varying architectures. Its adoption laid the foundation for the global phenomenon we now recognize as the internet, establishing a common language for devices to exchange data and ideas across vast distances.
(3) Diversity in Networks: From LANs to WANs
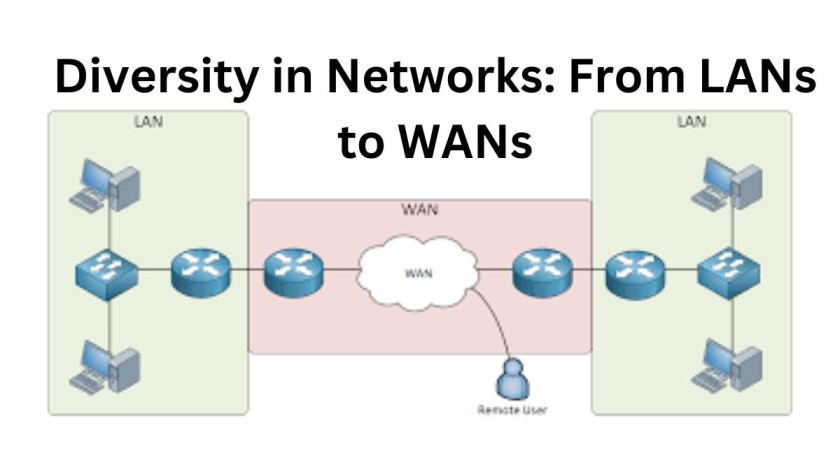
As computing power grew and the demand for connectivity soared, networks evolved to meet the diverse needs of users and organizations. Local Area Networks (LANs) emerged as the lifeblood of internal communication within confined spaces, facilitating data exchange among devices within a single location—an office building, university campus, or research facility. Conversely, Wide Area Networks (WANs) extended the reach of connectivity beyond geographical boundaries, connecting remote locations and enabling global communication on an unprecedented scale.
(4) The Internet Revolution: Connecting the World

The advent of the internet in the 1990s marked a paradigm shift in human communication and interaction. With the commercialization of the World Wide Web, the Internet transcended its origins as a research tool to become a global platform for commerce, communication, and collaboration. The proliferation of websites, email services, and multimedia content fueled an exponential increase in network traffic, driving the need for faster, more reliable connectivity solutions.
(5) Wireless Wonder: Unleashing Mobility

As the new millennium dawned, the world witnessed the dawn of a wireless revolution. Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular technologies liberated users from the confines of wired connections, enabling seamless communication and internet access on the go. The rise of smartphones and mobile devices accelerated this shift, ushering in an era of anytime, anywhere connectivity. With the advent of 3G, 4G, and now 5G networks, data speeds soared to unprecedented heights, paving the way for a new wave of innovation and connectivity.
(6) Future Horizons: Navigating the Digital Landscape

As we gaze towards the future, the horizon of computer network evolution stretches. The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, smart technologies, and interconnected systems heralds a new era of connectivity—one where every aspect of our lives is intertwined with the digital realm. Emerging technologies such as Software-Defined Networking (SDN), Edge Computing, and 6G networks promise to revolutionize the way we architect, deploy, and manage network infrastructure, ushering in an era of unprecedented speed, scalability, and security.
Features and Importance:

- Scalability: One of the paramount features of modern computer networks is their scalability. Networks must be able to accommodate growing numbers of users, devices, and data traffic without sacrificing performance or reliability.
- Reliability: In an interconnected world where downtime can spell disaster, reliability is of utmost importance. Network redundancy, fault tolerance, and robust error detection and correction mechanisms ensure uninterrupted communication and data exchange.
- Security: With cyber threats on the rise, network security has become a critical concern for organizations and individuals alike. Features such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols safeguard sensitive data and protect against unauthorized access and malicious attacks.
- Flexibility: Modern networks must be flexible and adaptable to meet the evolving needs of users and applications. Technologies such as virtualization, cloud computing, and Software-Defined Networking (SDN) enable dynamic provisioning of resources and on-demand scalability.
- Cost-effectiveness: Efficient use of resources and optimization of network infrastructure are essential for minimizing costs and maximizing return on investment. Network management tools, traffic-shaping algorithms, and energy-efficient protocols help reduce operational expenses and improve resource utilization.
Comparison:
- Speed: The evolution of computer networks has seen dramatic improvements in data transmission speeds, from the early days of dial-up internet to the lightning-fast speeds of fiber-optic broadband and 5G wireless networks.
- Coverage: While early networks were confined to limited geographical areas, modern networks provide ubiquitous coverage, spanning cities, countries, and continents. Technologies such as satellite communication and undersea cables have further expanded the reach of connectivity.
- Latency: With the advent of high-speed networks such as 5G, latency—the delay between sending and receiving data—has been greatly reduced, enabling real-time communication and immersive multimedia experiences.
- Security: As cyber threats continue to evolve, network security has become increasingly sophisticated, with advanced encryption algorithms, intrusion detection systems, and threat intelligence platforms protecting against a wide range of attacks.
- Reliability: Modern networks are designed with redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure uninterrupted operation in the event of hardware failures, network congestion, or malicious attacks. Redundant links, load balancing, and automatic failover mechanisms help maintain uptime and reliability.
conclusion:
The evolution of computer networks is a testament to human ingenuity and innovation. From humble beginnings to the dynamic digital landscape of today, networking has transformed the way we communicate, collaborate, and connect with the world around us. As we navigate the complexities of modern networking, let us embrace the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead, knowing that the journey of computer network evolution is far from over—and that the most exciting chapters are yet to be written.
Read more- Top 5 Operating System in Laptop


1 thought on “Computer Network Evolution”