Table of Contents
Introduction:
The advent of the digital era has brought about a paradigm shift in the way businesses and individuals interact with data, with cloud networking emerging as the backbone of modern IT infrastructures. By leveraging the power of cloud computing, organizations can effectively store, manage, and access their data from anywhere in the world, while minimizing upfront costs and maximizing scalability.
However, to fully harness the potential of cloud networking, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the different types of cloud networks and how they operate. From public clouds to private clouds, hybrid clouds, and multi-cloud environments, each type of cloud network has its unique strengths and weaknesses, making it crucial to choose the right network for your specific needs. By embarking on a journey to unravel the diverse landscapes of cloud networking, you can gain the knowledge and insights necessary to make informed decisions that align with your unique business requirements.
List of 4 Types of Cloud Networking:
(1) Public Cloud Networking:
In today’s fast-paced digital world, public cloud networking has become a vital component of business operations. It offers unmatched scalability and accessibility, allowing companies to leverage shared computing resources over the Internet. Providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform offer massive pools of computing resources that are reliable, secure, and highly available.
This type of networking provides businesses with unparalleled flexibility, cost-efficiency, and global reach. It is particularly beneficial for startups, small to medium enterprises (SMEs), and large corporations alike as it allows them to easily and efficiently deploy and manage their applications and services. Public cloud networking enables companies to achieve faster time-to-market, reduce capital expenses, and scale their operations in line with their business requirements. In summary, public cloud networking is a game-changer for businesses seeking to stay competitive in the digital landscape.
(2) Private Cloud Networking:
In recent years, private cloud networking has emerged as a highly effective solution for organizations that prioritize data privacy, security, and compliance. Unlike public clouds, which are shared by multiple organizations, private clouds are dedicated to a single entity. This exclusive environment affords greater control over infrastructure, ensuring that sensitive data remains shielded from external threats.
Private cloud networking can be hosted either on-premises or by a third-party provider, depending on the organization’s requirements. This flexibility allows companies to customize their private cloud infrastructure to meet their specific needs and regulatory requirements.
Private cloud networking is a preferred choice for industries such as finance, healthcare, and government, where regulatory compliance is paramount. These industries handle sensitive data that must be protected from unauthorized access, and private cloud networking provides the necessary level of security and control. In addition to enhanced security and compliance, private cloud networking also provides other benefits, such as better performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. With private cloud networking, organizations can scale their infrastructure as needed, without worrying about resource constraints or performance issues.
Overall, private cloud networking is an attractive option for organizations that require a high level of data privacy, security, and compliance. Its exclusive environment, enhanced control, and flexibility make it a compelling solution for industries that handle sensitive data and need to meet strict regulatory requirements.
(3) Hybrid Cloud Networking:
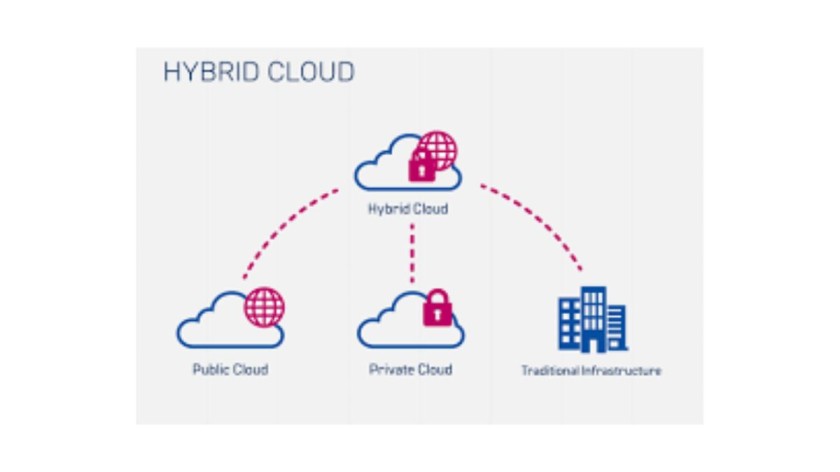
In the quest for the perfect synergy between flexibility and control, hybrid cloud networking emerges as a game-changer. Organizations can optimize workload placement, scalability, and performance by seamlessly integrating public and private cloud environments. Hybrid cloud networking empowers businesses to leverage the strengths of both worlds, enabling them to meet fluctuating demands, enhance disaster recovery capabilities, and maintain legacy systems while embracing innovation.
(4) Multi-Cloud Networking:

Diversification is the name of the game in multi-cloud networking, where organizations harness the power of multiple cloud providers simultaneously. By distributing workloads across various platforms, businesses mitigate vendor lock-in risks, enhance redundancy, and optimize performance. However, managing multiple cloud environments demands robust governance, orchestration, and interoperability strategies to ensure seamless operation and cost optimization.
Conclusion:
As we conclude our exploration of the diverse types of cloud networking, it’s evident that each model presents unique advantages and challenges. Whether you’re venturing into the cloud for the first time or seeking to optimize your existing infrastructure, understanding these nuances is key to unlocking the full potential of cloud technology. Embrace the possibilities, adapt to evolving landscapes, and empower your organization to thrive in the digital era.
By providing valuable insights into the intricacies of cloud networking, this blog aims to position your website as a go-to resource for individuals and businesses seeking knowledge in this niche. Remember to incorporate relevant keywords strategically throughout the content to enhance its SEO performance and improve visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs). With a well-crafted SEO-friendly blog and a comprehensive understanding of your niche, you’re poised to ascend to the top of Google search rankings and establish authority in the realm of cloud networking.
Read more- Discover the Top 10 Popular Car Accessories
FAQ:
(1) What is cloud networking?
Cloud networking refers to the practice of utilizing cloud computing resources to facilitate communication and data exchange between devices, applications, and users over the Internet. It encompasses a wide range of technologies and services designed to optimize network performance, scalability, and security in cloud-based environments.
(2) What is the primary function of a route table in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure networking service?
The primary function of a route table in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure networking service is to define the rules that dictate where network traffic should be directed within a virtual cloud network (VCN). Route tables contain route rules that specify destinations and the corresponding target destinations, such as internet gateways or virtual network appliances.
(3) What is the benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
The primary benefit of using cloud computing in networking is the ability to access scalable and flexible resources on-demand, allowing organizations to quickly adapt to changing network requirements without the need for significant upfront investments in infrastructure. Cloud networking also offers enhanced resilience, cost-efficiency, and global reach compared to traditional networking models.
(4) What is cloud networking, for example?
Cloud networking encompasses various networking technologies and services offered by cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). Examples include virtual private clouds (VPCs), load balancers, virtual private networks (VPNs), content delivery networks (CDNs), and software-defined networking (SDN) solutions.
(5) What is networking in cloud computing?
Networking in cloud computing refers to the process of establishing and managing connections between cloud-based resources, including virtual machines, databases, storage, and applications. It involves configuring network settings, defining access controls, ensuring data security, and optimizing network performance to support efficient communication and data exchange in cloud environments.
(6) Which of the following networking components can be used to host EC2 resources in the AWS cloud?
In the AWS cloud, Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances can be hosted using various networking components, including:
-Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs)
-Subnets
-Internet Gateways
-Route Tables
-Security Groups
-Network Access Control Lists (ACLs)
(7) Which of the following is used to achieve traffic separation in cloud networking?
Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) are commonly used to achieve traffic separation in cloud networking. VPCs allow organizations to create isolated network environments within the cloud, enabling them to control communication between different resources, segments, or departments while maintaining security and compliance.
(8) What is storage networking in cloud computing?
Storage networking in cloud computing involves the use of specialized network architectures and protocols to facilitate access to storage resources, such as object storage, block storage, and file storage, over the network. Storage networking enables organizations to efficiently store, retrieve, and manage data in the cloud, supporting various use cases ranging from backup and archival to data analytics and content delivery.
(9) How does cloud networking work?
Cloud networking works by leveraging virtualized network infrastructure, software-defined networking (SDN), and internet-based connectivity to enable communication and data exchange between cloud-based resources. It involves configuring network settings, defining access controls, and implementing network security measures to ensure seamless connectivity, performance, and reliability in cloud environments.
(10) Which of the following is not true about cloud service networking?
Without specific options provided, it’s challenging to determine which statement is not true about cloud service networking. However, common misconceptions may include:
-Cloud service networking is always less secure than on-premises networking.
-Cloud service networking is only suitable for large enterprises.
-Cloud service networking requires significant upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure.
(11) What is multi-cloud networking?
Multi-cloud networking refers to the practice of utilizing multiple cloud service providers (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP) simultaneously to distribute workloads, mitigate risks, and optimize costs. It involves orchestrating network connectivity, data flows, and management across different cloud environments to leverage the strengths of each provider and avoid vendor lock-in.
(12) What is a key distinguishing feature of networking in Google Cloud?
One key distinguishing feature of networking in Google Cloud is its global network infrastructure, which spans multiple continents and regions. Google Cloud’s network is designed for high performance, low latency, and scalability, leveraging Google’s extensive fiber-optic network backbone and edge locations to deliver fast and reliable connectivity to users worldwide.
(13) What is public cloud access networking?
Public cloud access networking refers to the mechanisms and technologies used to establish connectivity between on-premises networks or client devices and public cloud environments, such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform. It typically involves configuring virtual private networks (VPNs), direct connections, or internet-based connectivity options to facilitate secure and reliable access to cloud resources over the internet.
(14) What type of firewall rule(s) does Google Cloud’s networking support?
Google Cloud’s networking supports both ingress and egress firewall rules to control traffic entering and exiting virtual machine instances and other resources within a virtual private cloud (VPC) network. Firewall rules can be configured based on IP addresses, ports, protocols, and tags to enforce security policies and restrict unauthorized access to resources.
(15) What is a common approach to implementing load balancing in cloud-native networking?
A common approach to implementing load balancing in cloud-native networking is to use a cloud-based load balancer service provided by the cloud provider, such as Google Cloud Load Balancing, AWS Elastic Load Balancing, or Azure Load Balancer. These services distribute incoming traffic across multiple backend instances or services, ensuring high availability, scalability, and performance for cloud-based applications and services.

1 thought on “4 Types of Cloud Networking”